Understanding Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Cleveland Clinic Insights

Intro
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare yet significant form of skin cancer that warrants careful examination due to its aggressive nature. Originating from Merkel cells, which are specialized skin cells involved in the sensation of touch, MCC presents a distinct set of challenges for both diagnosis and treatment. The Cleveland Clinic, known for its advancements in dermatology and oncology, offers a vital perspective on overcoming the hurdles associated with this complex disease.
In exploring MCC, it is essential to understand its definition and the underlying scientific principles that govern its pathology. This article will delve into various aspects, including cutting-edge research, recent clinical trials, and comprehensive treatment options that reflect current best practices in patient care.
Through a systematic analysis and synthesis of relevant data from Cleveland Clinic, the aim is to enrich the audience's understanding of this malignancy, focusing on the critical role that multidisciplinary teams play in fostering effective management strategies.
Prelude to Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) is a significant topic due to its rarity and aggressive nature. Understanding this type of skin cancer is critical for several reasons. First, it is essential to increase awareness among healthcare professionals and the general public. Early detection can lead to better outcomes and may improve survival rates, making knowledge about the disease vital.
The increasing incidence of MCC represents a challenge for oncologists and dermatologists. This article aims to explore this cancer with insights from one of the leading institutions in the field. The Cleveland Clinic has made notable advancements in understanding and treating MCC, and their experiences can provide valuable lessons for both practitioners and patients.
Definition and Overview
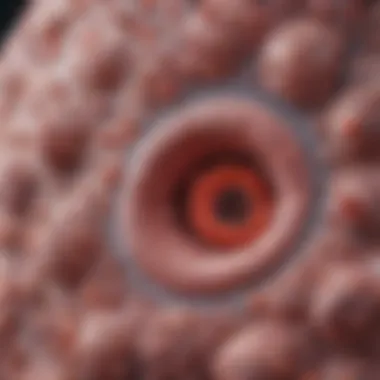
Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine skin cancer that typically arises in sun-exposed areas of the skin. The cancer stems from Merkel cells, which are specialized cells located in the epidermis. These cells are associated with the sensation of touch and can be influenced by several factors such as ultraviolet radiation and viral infections. MCC can appear as a firm, painless nodule, often mistaken for a benign skin lesion.
Patients may face challenges in diagnosis due to the nonspecific nature of symptoms. This emphasizes the need for healthcare providers to be aware of the condition, enabling them to distinguish it from other skin cancers.
Historical Context
The recognition of Merkel Cell Carcinoma as a distinct entity has evolved over the years. Initially described in the 1970s, the designation of MCC as a separate malignancy stemmed from its unique histology and clinical features. Research into this cancer has progressed, particularly concerning its association with the Merkel cell polyomavirus.
In the late 20th century, the role of UV exposure as a risk factor was established, enhancing the understanding of MCC’s etiology. Continuous research efforts have helped identify effective diagnostic methods and treatment strategies.
Understanding the historical context aids in appreciating the advancements in treatment options and ongoing clinical trials at well-established centers like the Cleveland Clinic. Through these insights, patients and professionals alike can navigate the complexities of this rare skin cancer more effectively.
Epidemiology of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Understanding the epidemiology of Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) provides crucial insights into its incidence, prevalence, and associated risk factors. This section discusses the patterns of MCC, revealing how these factors can inform both clinical practice and public health efforts.
Incidence and Prevalence
MCC is a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer. Its incidence has notably increased over recent decades. According to available data, the annual incidence of MCC in the United States is estimated at 0.6 to 1.5 per 100,000 people. The prevalence varies across different regions and demographic groups, affecting older adults more significantly than younger individuals. Understanding these statistics helps health professionals identify at-risk populations, thereby facilitating early detection and intervention strategies.
It is essential to recognize that while MCC remains a rare type of cancer, it is more frequently observed in individuals with light skin pigmentation. Additionally, the disease presents a higher incidence rate among those aged 50 and older. Factors such as geographical location can further influence prevalence, as areas with higher sun exposure may see increased cases.
Risk Factors
Several key risk factors have been identified in relation to the development of Merkel Cell Carcinoma, each contributing to a person's overall likelihood of developing this disease.
UV Radiation
One of the most significant risk factors for MCC is UV radiation exposure. Individuals with frequently sun-exposed skin are at a higher risk. UV radiation serves as a crucial contributor to skin damage, leading to mutations in DNA that can cause cancerous growths. Studies have indicated that people who live in sunny climates or who have a history of severe sunburns are particularly vulnerable. This aspect of UV radiation underpins the importance of protective measures such as sunscreen and protective clothing to mitigate risks.
Immune Suppression
People with weakened immune systems are also at increased risk for MCC. This immune suppression may arise from various causes, including autoimmune diseases, organ transplants, or certain medications that lower immune function. The weakened immune response can impair the body's ability to detect and destroy malignant cells. Acknowledging this risk factor highlights the necessity for rigorous monitoring and vigilance in at-risk populations.
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus
The Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCPyV) has been closely linked to the development of MCC. This virus can cause genetic changes in Merkel cells, leading to cancerous transformations. While many individuals carry MCPyV without developing MCC, those with compromised immune function or other risk factors are more susceptible. The understanding of this connection between the virus and cancer emphasizes the need for ongoing research and potential vaccination efforts against MCPyV as preventive strategies.
It is crucial to consider these epidemiological factors in both clinical care and further research into the mechanisms and treatments for Merkel cell carcinoma.
It is crucial to consider these epidemiological factors in both clinical care and further research into the mechanisms and treatments for Merkel cell carcinoma.
By exploring the epidemiology of MCC, we gain valuable insights that inform patient management strategies, contribute to public health education, and drive further research on prevention and treatment methods. Understanding these patterns is essential for health professionals and the community alike.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a critical component in understanding the disease's behavior and management. Recognizing the signs and symptoms is vital for early detection and intervention. Patients often present with various indicators that can vary widely in their expression, making it essential for healthcare providers to maintain a high index of suspicion, particularly in at-risk populations. Effective clinical presentation encompasses both the common symptoms experienced by individuals and the critical findings observed during physical examinations.
Common Symptoms
Merkel cell carcinoma typically presents as a painless, firm, and rapidly growing skin lesion. The most common symptoms include:
- Nodular Mass: This is often the first noticeable sign. The bump may vary in color ranging from skin-toned to red or purple.
- Ulceration: Some masses may become ulcerated, leading to oozing or bleeding as the cancer advances.
- Changes in Skin Texture: The skin over or surrounding the lesion may appear different from the surrounding skin. This alteration can manifest as shiny or smooth surfaces.
- Lymph Node Involvement: As the disease progresses, swollen lymph nodes in adjacent areas may occur. Patients may notice lumps in the neck, armpit, or groin regions.
These symptoms call for prompt medical evaluation. Patients or health providers should not overlook any new or unusual skin changes. Any patient with risk factors or concerning skin growth should seek a dermatologist’s expertise.
Physical Examination Findings


During the physical examination, clinicians look for specific features that may confirm the suspicion of Merkel cell carcinoma. This examination is essential because many patients may have initially misinterpreted their lesions as benign. Key findings include:
- Skin Lesions: The lesions identified may appear as dome-shaped nodules, which are typically palpable and may be tender to touch.
- Regional Lymphadenopathy: A thorough examination may reveal enlarged lymph nodes, indicating potential metastasis. Physicians often assess surrounding lymphatic areas for signs of involvement.
- Asymmetry and Borders: Visual assessment of the lesion's borders and symmetry may hint toward malignancy. Traditional characteristics of benign moles can differ significantly in MCC.
- Variation in Coloration: The lesion might show a mix of colors or hues, unlike a typical benign growth, which usually has uniform color.
The importance of careful assessment during the physical examination cannot be underestimated. Accurate detection and assessment often dictate effective treatment regimens and outcomes.
The importance of careful assessment during the physical examination cannot be underestimated. Accurate detection and assessment often dictate effective treatment regimens and outcomes.
In essence, a thorough understanding of clinical presentation aids in understanding Merkel cell carcinoma better. Healthcare professionals equipped with the knowledge of symptoms and examination findings can expedite the diagnostic process, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Diagnosis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) plays a vital role in the journey of managing this aggressive skin cancer. Due to its rarity and the potential for rapid progression, accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment planning. Medical professionals must consider various diagnostic techniques to ensure that MCC is identified promptly. Understanding these methods not only improves patient outcomes but also aids in establishing a seamless treatment pathway based on precise information.
Early detection can substantially impact the prognosis, making the subsequent management of the disease more successful.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
CT Scan
A CT scan utilizes X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. This imaging technique is beneficial in diagnosing MCC, as it can help visualize the extent of tumor spread in tissues and lymph nodes. One key characteristic of the CT scan is its rapid acquisition of multiple images, which provides timely insights into lesion location and size. This aspect is particularly helpful for staging the cancer and planning appropriate interventions.
A notable advantage of CT scans is their high sensitivity in detecting abnormalities in soft tissues, making them a favored option for oncological assessments. However, a disadvantage is the exposure to radiation, which necessitates weighing the risks and benefits, especially in a cancer patient.
PET Scan
The PET scan, or positron emission tomography, works differently than conventional imaging techniques. It helps in detecting metabolic activity in tissues, often highlighting areas where cancer cells are more active. This is particularly valuable in MCC, as it provides functional information about tumor aggressiveness. The PET scan is popular in oncology because it can reveal metastases that might not be visible through other imaging methods.
One unique feature of the PET scan is its ability to assess both the primary tumor and distant sites simultaneously, which aids in comprehensive staging. Despite its benefits, the cost of PET scans can be a limitation, and it may not be as widely available as other imaging options.
Histological Evaluation
Biopsy Types
Biopsy types are essential components of the diagnostic process for MCC. A biopsy involves taking a small sample of tissue for pathological examination. Different biopsy methods can be applied, including excisional, incisional, and fine-needle aspiration biopsies. Each type offers unique benefits and limitations depending on the clinical context.
A key feature of biopsies is their ability to provide definitive histological confirmation of MCC, which is crucial for tailored treatment approaches. Most importantly, an excisional biopsy can often remove the entire lesion, thus serving a dual purpose of diagnosis and potential curative treatment. On the downside, complications such as infection and scarring can occur, depending on the method used.
Pathological Features
Pathological features of MCC are crucial for diagnosis and understanding the disease's behavior. Upon microscopic examination, specific characteristics such as cell morphology, nuclear atypia, and mitotic activity can indicate the presence and aggressiveness of MCC. This histological evaluation allows for precise classification of the tumor, guiding treatment decisions.
Importantly, marked cellular density and perivascular infiltration are generally observed in MCC samples. Such identifiable features aid pathologists in confirming the diagnosis quickly. However, relying solely on histological assessment may sometimes lead to misinterpretation due to overlapping features with other skin cancers.
Accurate diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma hinges on the combination of imaging techniques and thorough histological analysis.
Accurate diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma hinges on the combination of imaging techniques and thorough histological analysis.
Treatment Options at the Cleveland Clinic
Treatment options for Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) at the Cleveland Clinic are vital for patient outcomes. The clinic offers a comprehensive array of therapies tailored to the specific needs of each patient. Surgical methods, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy comprise a multi-faceted approach to combating this aggressive skin cancer. Each therapy targets different aspects of the disease process, contributing to improved survival rates and quality of life. The significance of personalized treatment plans cannot be understated; they are informed by clinical research and multidisciplinary collaboration.
Surgical Approaches
Wide Local Excision
Wide local excision is a prevalent technique in the surgical management of MCC. It involves removing the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete resection. This method is essential because it minimizes the risk of local recurrence by addressing the tumor at its root. The key characteristic of wide local excision is its thoroughness, ensuring that no malignant cells remain near the surgical site. For many patients, it represents the first line of defense against MCC.
Advantages of Wide Local Excision:
- Reduces the risk of recurrence by targeting surrounding healthy tissue.
- Can often be performed as an outpatient procedure, minimizing hospital stays.
- Provides a definitive diagnosis and enables immediate pathological evaluation.
However, there are disadvantages to consider. The procedure may require significant cosmetic considerations, especially when tumors occur in prominent areas. Patients might also experience discomfort and require pain management post-operatively.
Lymph Node Dissection
Lymph node dissection plays an important role in managing Merkel cell carcinoma through the assessment and removal of affected lymph nodes. When MCC is suspected to have metastasized, dissection is crucial for staging and treatment planning. The key feature of lymph node dissection is its capacity to offer crucial information about the extent of the disease and possible treatment modifications.
Advantages of Lymph Node Dissection:
- Provides valuable staging information that guides further treatment.
- Can significantly reduce the burden of disease if regional nodes are involved.
However, this approach is not without risks. Potential complications may include lymphedema and other surgical risks related to anesthesia. Overall, lymph node dissection contributes to a comprehensive treatment strategy, particularly for patients with advanced-stage MCC.


Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is an integral part of the treatment plan for patients with Merkel cell carcinoma. It is frequently used when surgical options alone are deemed insufficient. The primary role of radiation therapy is to target residual cancer cells in the local region, further minimizing the risk of recurrence. This modality is especially beneficial for patients with a higher risk of local relapse due to positive margins post-surgery or extensive disease before surgical intervention.
Radiation can be delivered via external beam radiotherapy or interstitial brachytherapy, depending on the tumor's characteristics and location. Its importance lies not only in its direct ability to kill cancer cells but also in its role in enhancing overall local control of the disease.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapies
Chemotherapy and targeted therapies have become critical as part of the treatment landscape for MCC, especially in advanced stages. While chemotherapy involves using cytotoxic agents to inhibit cancer cell growth, targeted therapies focus on specific molecular targets associated with cancer progression.
Common Chemotherapy Regimens:
- Doxorubicin
- Cisplatin
Targeted therapies, such as immunotherapies, aim to unleash the body’s immune system against the tumor. Studies have shown promising results with drugs like pembrolizumab and nivolumab in treating advanced Merkel cell carcinoma.
Integration of these treatment options at the Cleveland Clinic emphasizes a personalized approach, aiming to enhance patient survival rates and improve quality of life. Each therapy brings unique advantages and must be considered within the context of the individuals' overall health and cancer progression.
Multidisciplinary Care Approach
The management of Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) requires a multidisciplinary care approach. This strategy is essential because MCC is a complicated disease that involves several systems in the body. A collective effort from various specialists ensures that patient care is comprehensive and tailored to meet individual needs, enhancing outcomes and quality of life.
Role of Dermatologists
Dermatologists play a crucial role in the early detection and treatment of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Their expertise in skin disorders allows them to recognize early signs of MCC, which can be pivotal for successful treatment. They conduct biopsies to confirm diagnoses and guide surgical interventions. With their knowledge, dermatologists also help in planning post-operative care and monitoring for recurrence.
Their ongoing involvement is vital. They not only treat the primary skin lesions but also educate patients about skin care and protection against UV radiation. Dermatologists help ensure that patients are aware of the importance of regular follow-up visits and skin checks.
Collaboration with Oncologists
Oncologists are integral to the management of Merkel Cell Carcinoma due to their specialized training in cancer treatment. Their role includes determining the need for chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted treatments based on the individual case.
Collaboration between dermatologists and oncologists enables the development of a cohesive treatment plan. This partnership allows for data sharing that can inform clinical decisions, such as the timing of radiotherapy or the necessity of chemotherapy post-surgery. Moreover, oncologists are often involved in clinical trials, which may provide patients with access to innovative therapies that are not yet widely available.
This collaborative framework is significant because it ensures that every aspect of a patient's condition is understood and treated with the latest evidence-based strategies. Such an approach not only increases the chances of improved survival rates but also helps in managing side effects more effectively, thus supporting the overall well-being of the patient.
"The landscape of treating Merkel Cell Carcinoma is best navigated through a team of specialized professionals working towards a common goal — the patient's recovery and health."
"The landscape of treating Merkel Cell Carcinoma is best navigated through a team of specialized professionals working towards a common goal — the patient's recovery and health."
In summary, the multidisciplinary care approach in the treatment of Merkel Cell Carcinoma is fundamental. It encompasses the insights from dermatology and oncology, thereby enhancing the scope of treatment and ensuring comprehensive care for those affected by this rare skin cancer.
Ongoing Research and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research and clinical trials play a critical role in advancing the understanding and treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Given its rarity and aggressive nature, MCC presents unique challenges for researchers and clinicians. Studies aim to explore new diagnostic methods, treatment approaches, and the underlying biology of the disease. The Cleveland Clinic is at the forefront of these efforts, contributing valuable insights to the medical community.
Research contributes to the identification of better prognostic factors which help predict patient outcomes. It also allows for clinical trials that facilitate the assessment of new therapies or combinations of treatments that may improve survival rates and quality of life for patients. By investigating different treatment modalities, researchers seek to optimize protocols that cater to the specific needs of MCC patients.
Additionally, engaging in clinical trials is instrumental in offering patients access to cutting-edge therapies. This can be crucial for those who do not respond well to standard treatments. Understanding that every patient’s cancer behaves differently, these tailored approaches can lead to significant improvements in therapeutic outcomes.
"Clinical trials are essential for advancing treatments, especially for rare diseases like Merkel cell carcinoma. They provide hope through innovation and targeted therapies."
"Clinical trials are essential for advancing treatments, especially for rare diseases like Merkel cell carcinoma. They provide hope through innovation and targeted therapies."
Moreover, participation in clinical trials not only benefits individual patients but also contributes to the broader understanding of MCC. Insights gained from these trials may lead to breakthroughs that enhance treatment options for future patients. As part of their commitment to patient care, the Cleveland Clinic emphasizes the importance of continuous research and collaboration across disciplines.
Current Clinical Trials at Cleveland Clinic
At the Cleveland Clinic, a number of clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate various treatment strategies for Merkel cell carcinoma. These trials include:
- Investigational Therapies: New drugs and treatments that have not yet received approval.
- Combination Therapies: Trials that test various combinations of existing treatments to ascertain efficacy and safety.
- Immunotherapy Approaches: Focusing on harnessing the body’s immune system to fight MCC.
These clinical trials include carefully designed protocols aimed at assessing efficacy, safety, and patient outcomes. Each study is critically overseen by experienced professionals who ensure that participants receive optimal care throughout their involvement. This structured approach minimizes risks while maximizing potential benefits to participants.
Innovations in Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy presents a promising frontier in the treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma. Recent advances have highlighted the potential of harnessing the immune system more effectively against this aggressive form of skin cancer. Cleveland Clinic researchers are exploring various innovative immunotherapeutic approaches, which include:
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Drugs that block proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells.
- Adoptive Cell Therapy: A method that enhances the body’s immune response by using modified T-cells.
- Vaccination Strategies: Researchers are investigating therapeutic vaccines designed to stimulate an immune response specifically targeting Merkel cell carcinoma.
These innovations in immunotherapy reflect a tailored approach to treatment, capable of providing significant benefits for patients who may not respond well to conventional therapies. The potential for long-lasting responses and reduced side effects positions immunotherapy as a key area of focus in ongoing research.
In summary, ongoing research and clinical trials are essential to improving our understanding and management of Merkel cell carcinoma. By concentrating efforts on innovative therapies and collaborative research, institutions like Cleveland Clinic pave the way for better outcomes for patients afflicted by this rare and complex disease.
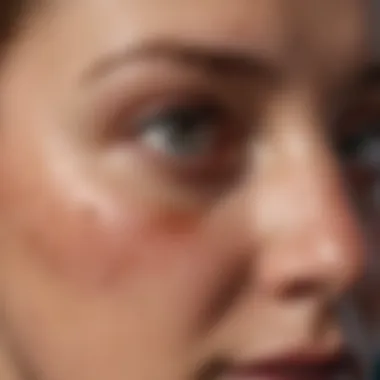

Prognosis and Follow-up Care
Prognosis and follow-up care are critical components in the management of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Understanding the expected outcomes and the strategies for long-term monitoring can significantly affect a patient's quality of life. The prognosis for MCC can vary widely based on several factors. Hence, clinicians must evaluate patients thoroughly to determine the best approach to care.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several elements can influence the prognosis of patients diagnosed with MCC. These include:
- Tumor Size: Larger tumors typically have a worse prognosis. The staging of the carcinoma at diagnosis plays a significant role in predicting the outcome.
- Lymph Node Involvement: The presence of metastatic disease in lymph nodes indicates a more aggressive form of cancer and is associated with decreased survival rates.
- Immune Status: Patients with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those on immunosuppressive therapies, often face poorer prognoses.
- Treatment Response: The effectiveness of initial treatments, including surgery, radiation, and immunotherapy, can also be a predictive factor. Patients responding well to treatment may have an improved prognosis.
Research indicates that factors such as age and overall health at the time of diagnosis can also influence outcomes. Awareness of these variables helps healthcare providers offer tailored treatment plans.
Importance of Monitoring
The importance of regular monitoring for patients with a history of MCC cannot be overstated. Regular follow-ups allow for the early detection of recurrence or metastasis, which can be critical for intervention. Key reasons include:
- Early Detection: Routinely scheduled check-ups can identify new lesions or changes in existing ones, enabling timely re-treatment.
- Surveillance for Metastatic Disease: As MCC can spread beyond the skin, monitoring allows for intervention before the cancer advances significantly.
- Adjustment of Treatment Plans: Ongoing assessment of the patient’s response to treatment can help identify if adjustments are necessary, whether through changing medication or incorporating new therapies.
"Regular follow-up is essential in managing Merkel cell carcinoma, given its aggressive nature and potential for recurrence."
"Regular follow-up is essential in managing Merkel cell carcinoma, given its aggressive nature and potential for recurrence."
Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare teams about any new symptoms or concerns, as this active participation in their care enhances monitoring effectiveness. Follow-up care typically includes physical examinations, imaging studies, and possibly laboratory tests to evaluate the overall health and monitor for signs of recurrence.
In summary, the prognosis of Merkel cell carcinoma hinges on a variety of factors, making ongoing follow-up care necessary for managing this rare and aggressive cancer. Monitoring not only aids in detecting recurrence but also fosters an environment for adjusting treatment as needed.
Patient Education and Support
Education is a fundamental component in the management of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Patient education empowers individuals to understand their diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of follow-up care. When patients are well-informed, they become active participants in their healthcare. This not only enhances their quality of life but also helps in making informed decisions that align with their values and preferences.
Effective patient education involves providing clear, accessible information about the disease. Patients should comprehend the nature of Merkel cell carcinoma, including its aggressive behavior and potential treatment pathways. It is crucial for them to grasp the implications of various therapies on their health and daily living.
"Knowledge is power, especially in navigating complex health conditions like Merkel cell carcinoma, where informed choices can significantly affect outcomes."
"Knowledge is power, especially in navigating complex health conditions like Merkel cell carcinoma, where informed choices can significantly affect outcomes."
Support services play a vital role in reinforcing education. They provide practical assistance and psychological support to patients and their families. This multifaceted approach helps alleviate anxiety and enhances adherence to treatment regimens.
Resources Available at Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic offers a wealth of resources tailored for patients diagnosed with MCC. Educational materials are readily available, encompassing brochures, online content, and access to webinars. These resources cover essential topics, such as:
- Overview of Merkel cell carcinoma
- Treatment options and clinical trials
- Side effects management
- Lifestyle and dietary recommendations
One-on-one consultations with specialized healthcare providers are also available. These meetings allow patients to ask questions relevant to their specific situations and to receive tailored advice.
Additionally, the Cleveland Clinic has a dedicated website section for cancer patients, which includes:
- Frequently asked questions
- Links to peer-reviewed articles on MCC
- Guides to understand lab results and imaging studies
- Information on financial assistance for treatment costs
Support Groups and Counseling
Support groups provide a platform for patients to connect with others experiencing similar challenges. Sharing experiences can markedly decrease feelings of isolation associated with a rare diagnosis like Merkel cell carcinoma. The Cleveland Clinic hosts regular support groups, facilitated by trained professionals, where patients can discuss their concerns, fears, and successes in a safe environment.
Counseling services are also a critical element of support. Professional counselors are available to help patients process their feelings and develop coping strategies. They assist in managing the emotional and psychological burdens that may arise during cancer treatment. Topics often covered include:
- Adjusting to the diagnosis
- Managing treatment-related anxieties
- Communicating effectively with family and friends
- Building resilience in the face of adversity
Overall, patient education and support at the Cleveland Clinic are structured to empower individuals, ensuring they receive all necessary information and emotional support throughout their cancer journey.
Ending
The conclusion of this article holds significant importance as it encapsulates essential insights into Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) and its multifaceted nature. One of the key elements discussed is the aggressive behavior of MCC, which necessitates early diagnosis and prompt therapeutic interventions. The unique characteristics of this rare skin cancer, such as its association with Merkel cell polyomavirus and various risk factors, underscore the need for continued research and greater awareness among both medical professionals and patients.
A thorough summary also highlights the wealth of information presented in the previous sections. Effective multidisciplinary care is pivotal for managing MCC, involving collaboration between dermatologists, oncologists, and researchers. This integrated approach leads to optimal treatment outcomes and improved patient experiences.
Moreover, the ongoing research and clinical trials conducted at esteemed institutions like the Cleveland Clinic are worth noting. These initiatives aim to innovate current treatment modalities, particularly in the realm of immunotherapy. This exploration of novel treatment options will be crucial as the medical community seeks to understand and combat this aggressive form of cancer.
Understanding the dynamics of prognosis and follow-up care further emphasizes the importance of vigilant monitoring and patient education. Patients benefit from knowing the resources available to them, fostering an environment of support and empowerment.
In summary, the conclusions drawn in this article not only elucidate the complexities of Merkel cell carcinoma but also serve as a call to action for higher awareness, ongoing research, and enhanced patient support.
Summary of Key Insights
- Aggressive Nature: Merkel cell carcinoma is recognized for its aggressive nature requiring immediate attention.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis: Early detection is crucial for improving prognosis and treatment outcomes.
- Multidisciplinary Care: Collaboration among various specialists enhances care quality.
- Research Initiatives: Ongoing studies at the Cleveland Clinic are vital for innovation in treatment.
- Patient Education: Awareness of available resources aids patient empowerment and support.
"Effective management of Merkel cell carcinoma hinges on a well-coordinated approach and continuous research to uncover effective therapies."
"Effective management of Merkel cell carcinoma hinges on a well-coordinated approach and continuous research to uncover effective therapies."
This conclusion emphasizes the relevance of understanding MCC, and it aims to motivate readers to engage with ongoing research and apply knowledge to improve patient care.







